Pathways of Effects
Fish and Fish Habitat Protection Program (FFHPP) Pathways of effects diagrams have been updated
Pathways of effects (PoE) diagrams are used to describe how projects in or near water can affect fish and fish habitat. Each diagram illustrates the chain of events that takes place in the aquatic environment when a work, undertaking or activity takes place.
PoE diagrams are an important tool for completing a Request for Review Form as they can help to:
- identify project risks to fish and fish habitat
- inform proponents in the development of avoidance and mitigation measures needed to manage those risks
- describe potential harmful impacts that may occur if risks are not avoided or mitigated
They have been peer reviewed* by expert scientists through the Canadian Science Advisory Secretariat and are used by the Fish and Fish Habitat Protection Program to conduct risk assessments when reviewing proposed projects and when developing Standards and codes of practice.
On this page
- Use of machinery on land/alteration of riparian vegetation
- Use of machinery in water
- Placement of materials in water
- Removal of materials and aquatic vegetation from water
- Water level/flow modification
- Water diversion
- Dewatering
- Detonation in or near water
- Introduction of underwater noise
The 9 PoE diagrams below represent the most common risk causes (top box) and pressures (round endpoints) on fish and fish habitat that can result from works, undertakings and activities in or near water:
Use of machinery on land/alteration of riparian vegetation
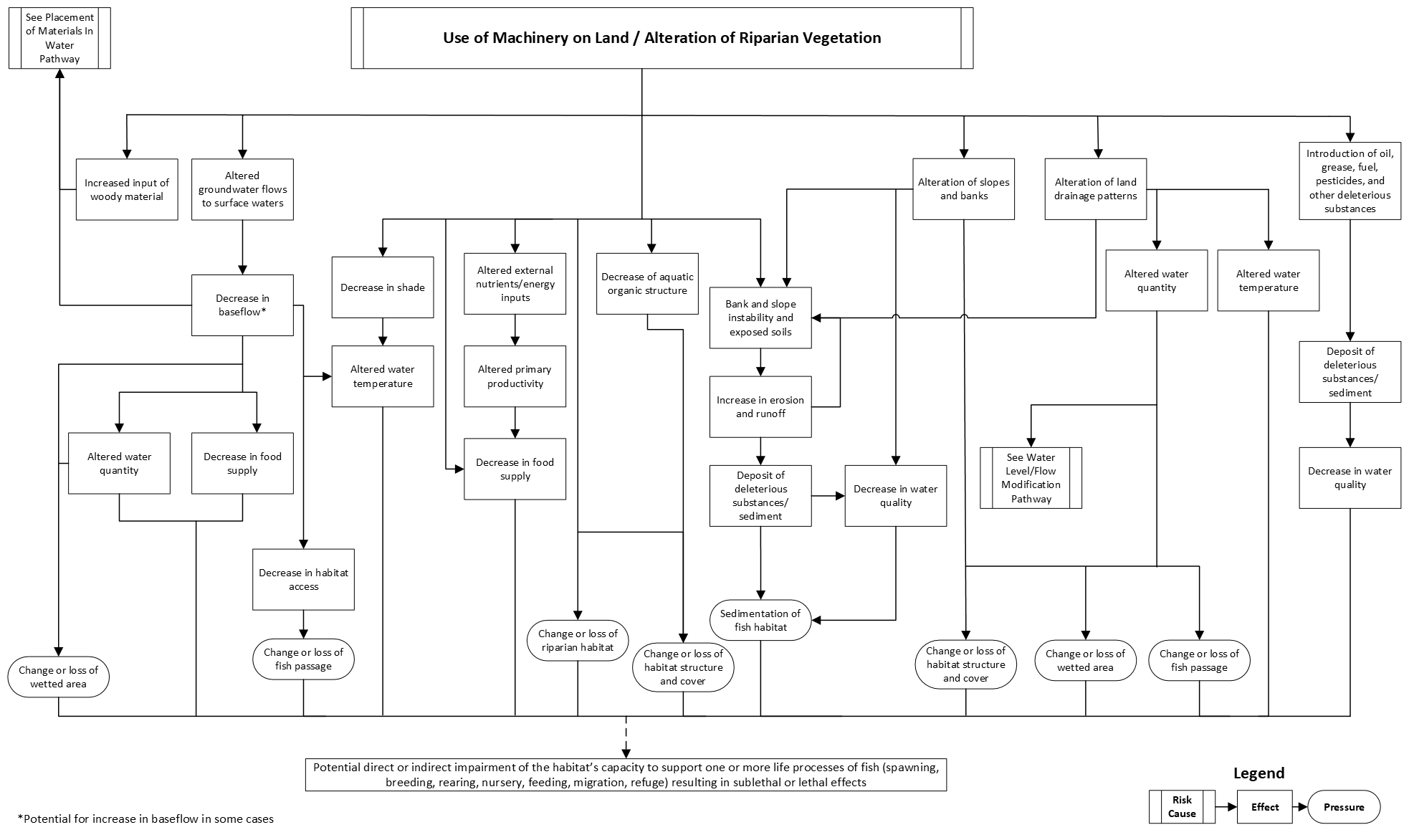
This pathway illustrates the chain of events that takes place in an aquatic ecosystem when works, undertaking and activities (WUAs) are conducted in the riparian zone. Common WUAs that require the use of machinery on land and/or the alteration of riparian vegetation include:
- grading
- excavating
- grubbing
- vegetation clearing and maintenance
- vegetation planting and seeding
- stockpiling
- construction
- repair and maintenance of infrastructure
- construction of access routes
If not managed, the use of machinery on land and alteration of riparian vegetation can result in:
- sedimentation of fish habitat
- changes to, or losses of:
- riparian habitat
- habitat structure and cover
- fish passage
- wetted area
These pressures have the potential to impair the habitat’s capacity to support the life processes of fish. Sublethal effects to fish (for example, injury and stress) and fish mortality are also possible if protection measures are not put in place.
Use of machinery in water
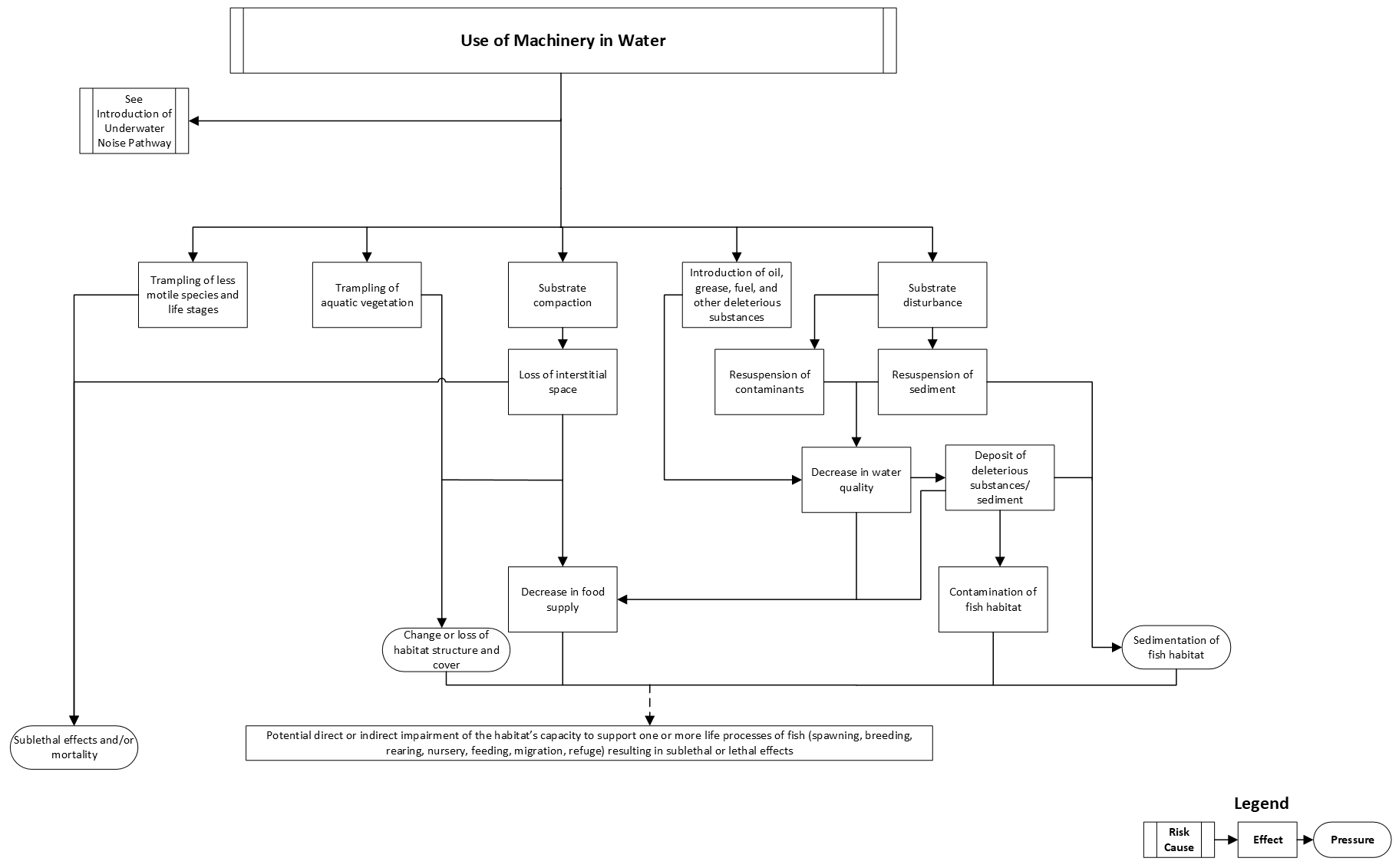
This pathway illustrates the chain of events that takes place in an aquatic ecosystem when machinery is used in water. Common works, undertakings and activities (WUAs) that require the use of machinery in water include:
- use of industrial equipment for dredging
- channel excavation
- oil and gas exploration and extraction
- mining, power generation (for example, wind, tidal and hydro)
- construction, repair and maintenance of infrastructure
If not managed, the use of machinery in water can result in:
- sedimentation of fish habitat
- changes to, or losses of:
- habitat structure and cover
These pressures have the potential to impair the habitat’s capacity to support the life processes of fish. Sublethal effects to fish (for example, injury and stress) and fish mortality are also possible if protection measures are not put in place.
Placement of materials in water
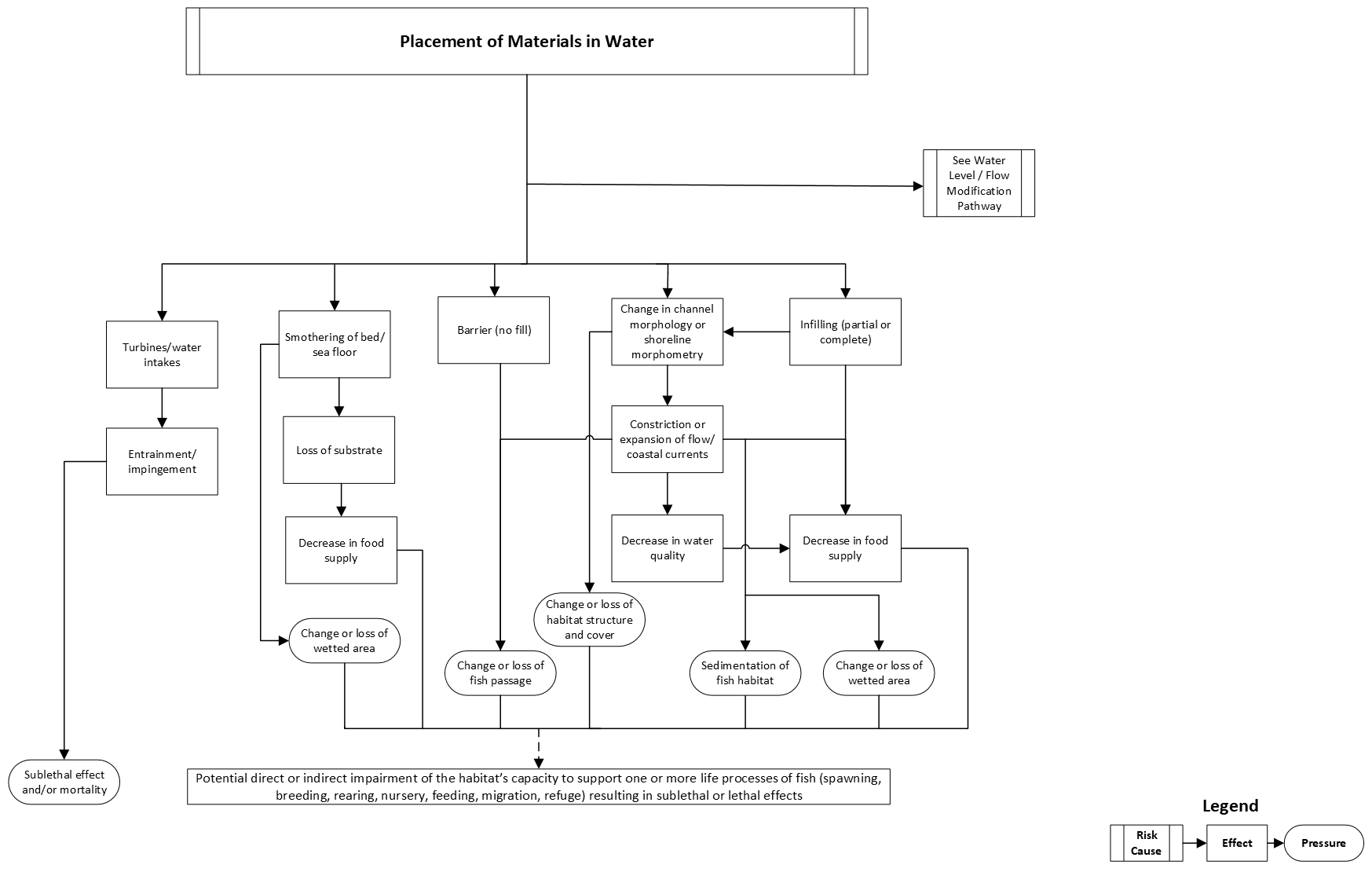
This pathway illustrates the chain of events that takes place in an aquatic ecosystem when materials are placed in the water.
Materials can be organic, for example:
- logs
- rocks
or human-made structures, for example:
- docks
- dams
- culverts
- pipelines
- abutments
- piers
- wharves
If not managed, the placement of materials in water can result in:
- sedimentation of fish habitat
- changes to, or losses of:
- habitat structure and cover
- fish passage
- wetted area
These pressures have the potential to impair the habitat’s capacity to support the life processes of fish. Sublethal effects to fish (for example, injury and stress) and fish mortality are also possible if protection measures are not put in place.
Removal of materials and aquatic vegetation from water
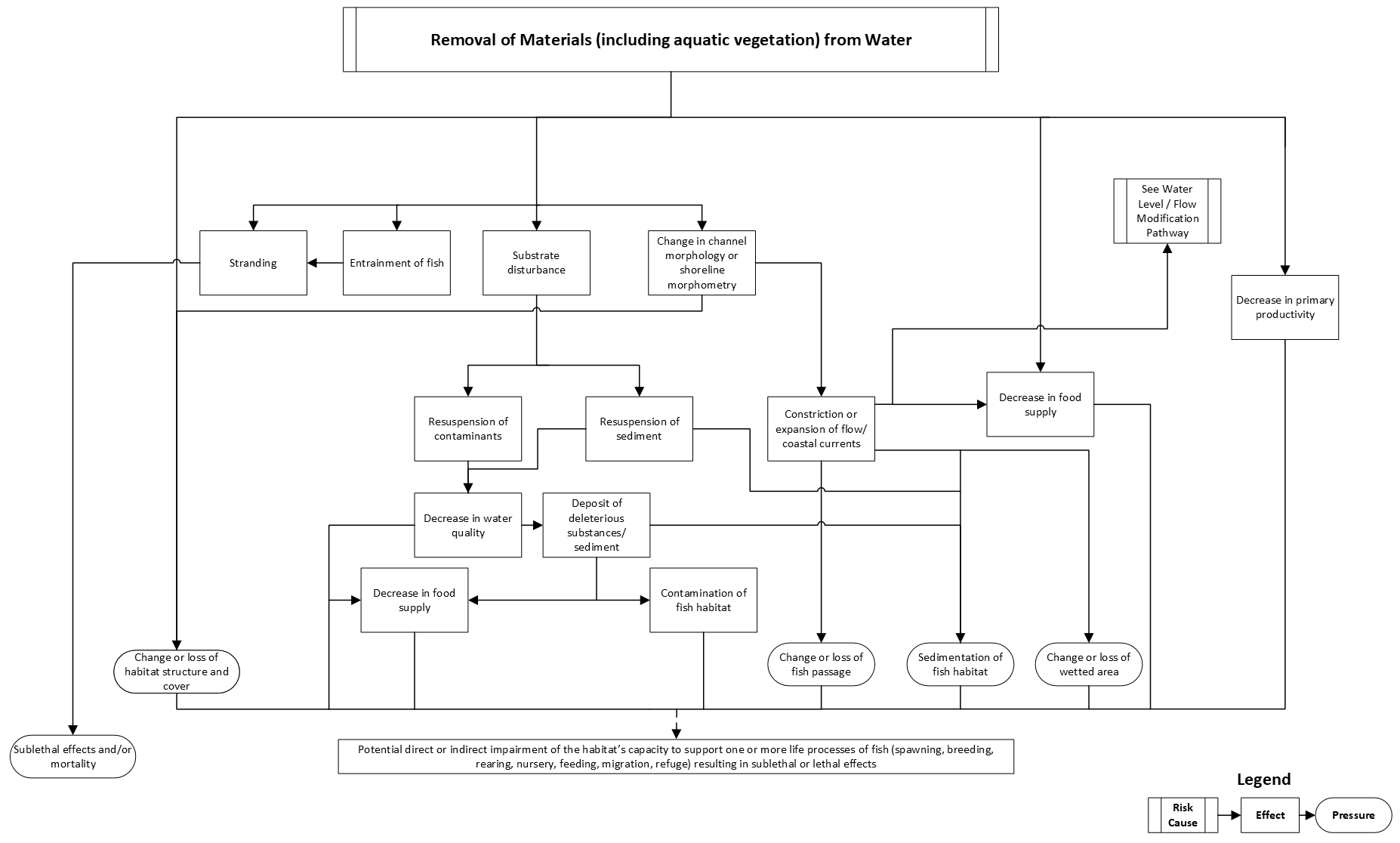
This pathway illustrates the chain of events that takes place in an aquatic ecosystem when materials are removed from the water.
Materials can be organic, for example:
- woody material
- logs
- aquatic vegetation
- sediment
or human-made structures, for example:
- docks
- dams
- culverts
- pipelines
- bridges
- piers
- wharves
If not managed, the removal of materials from the water can result in:
- sedimentation of fish habitat
- changes to, or losses of:
- habitat structure and cover
- fish passage
- wetted area
These pressures have the potential to impair the habitat’s capacity to support the life processes of fish. Sublethal effects to fish (for example, injury and stress) and fish mortality are also possible if protection measures are not put in place.
Water level/flow modification
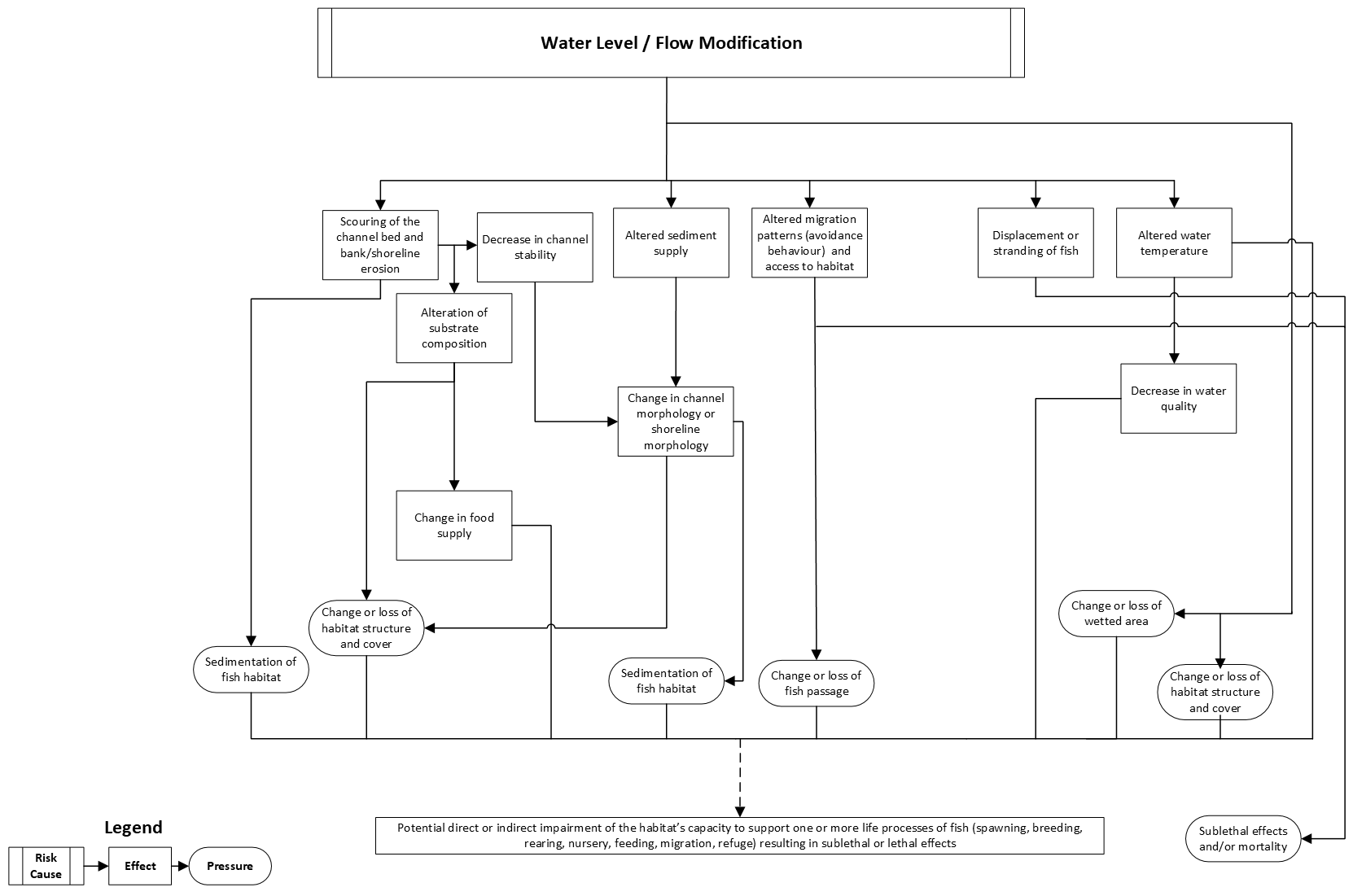
his pathway illustrates the chain of events that takes place in an aquatic ecosystem when water levels and flows are modified. Common works, undertakings and activities (WUAs) that involve modifying flows and water levels can include:
- dam construction and repair
- water extraction
- water management
- irrigation
- hydropower plant
If not managed, water level and flow modifications can result in:
- sedimentation of fish habitat
- changes to, or losses of:
- habitat structure and cover
- fish passage
- wetted area
These pressures have the potential to impair the habitat’s capacity to support the life processes of fish. Sublethal effects to fish (for example, injury and stress) and fish mortality are also possible if protection measures are not put in place.
Water diversion
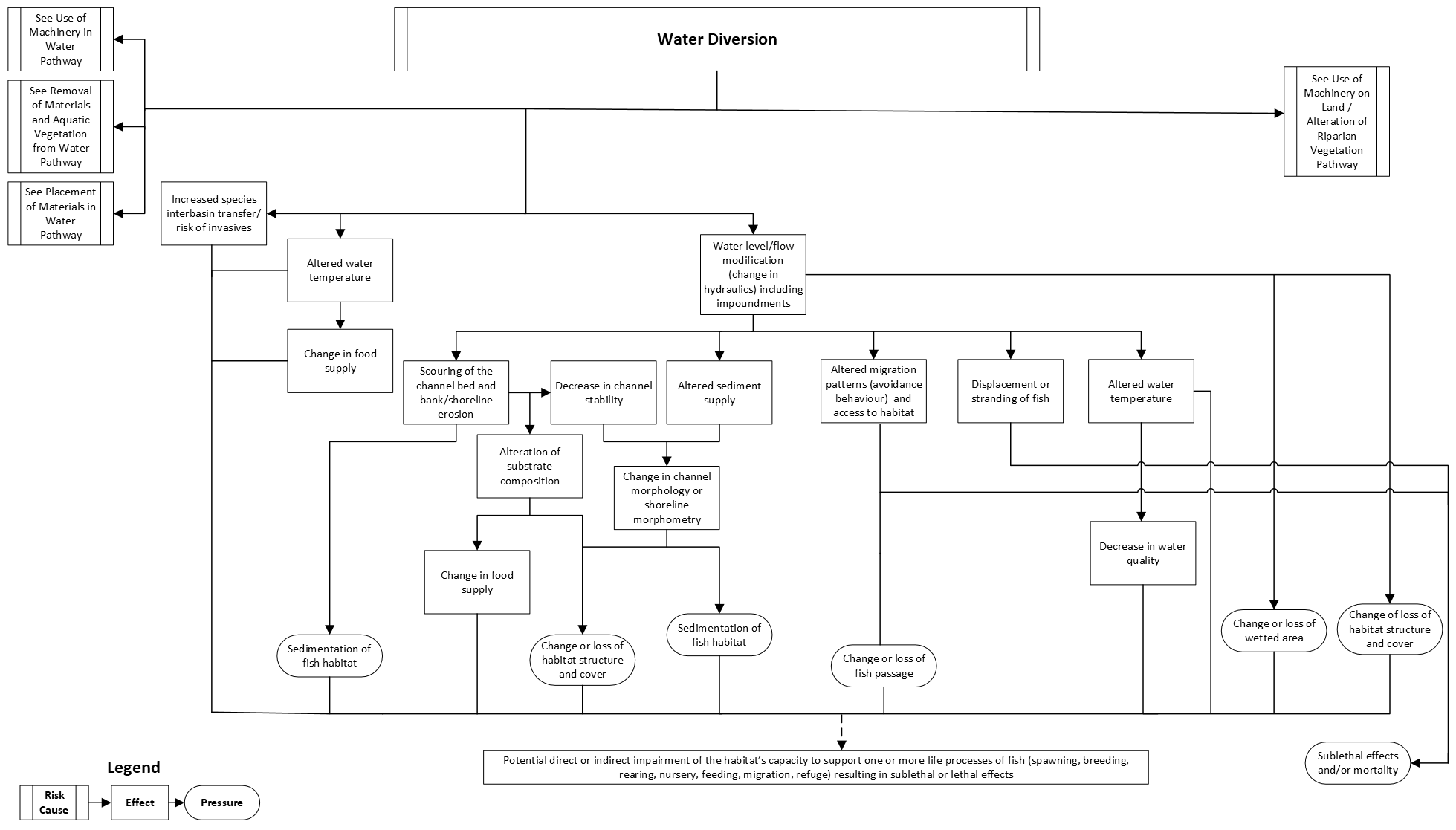
This pathway illustrates the chain of events that takes place in an aquatic ecosystem when water is diverted. Common works, undertakings and activities (WUAs) that involve water diversion include:
- stream realignments
- dams (power generation)
- mining
- culverts
- bridges
- pipelines
If not managed, water diversion can result in:
- sedimentation of fish habitat
- changes to, or losses of:
- habitat structure and cover
- fish passage
- wetted area
These pressures have the potential to impair the habitat’s capacity to support the life processes of fish. Sublethal effects to fish (for example, injury and stress) and fish mortality are also possible if protection measures are not put in place.
Dewatering
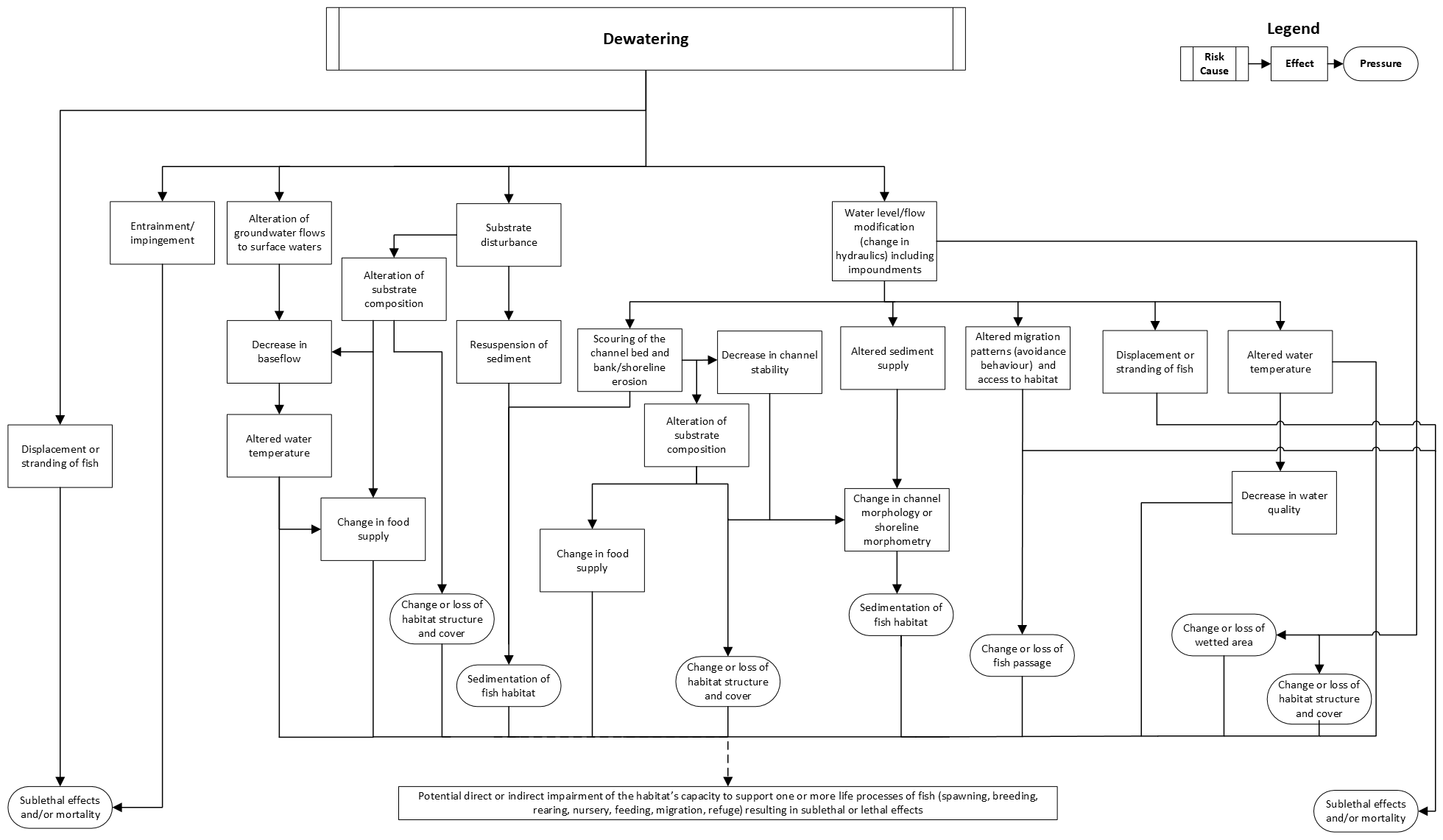
This pathway illustrates the chain of events that takes place in an aquatic ecosystem when areas containing fish habitat are dewatered. Common works, undertakings and activities (WUAs) that involve dewatering include:
- water extraction
- mining
- construction
- repair and maintenance of infrastructure
If not managed, dewatering can result in:
- sedimentation of fish habitat
- changes to, or losses of:
- habitat structure and cover
- fish passage
- wetted area
These pressures have the potential to impair the habitat’s capacity to support the life processes of fish. Sublethal effects to fish (for example, injury and stress) and fish mortality are also possible if protection measures are not put in place.
Detonation in or near water
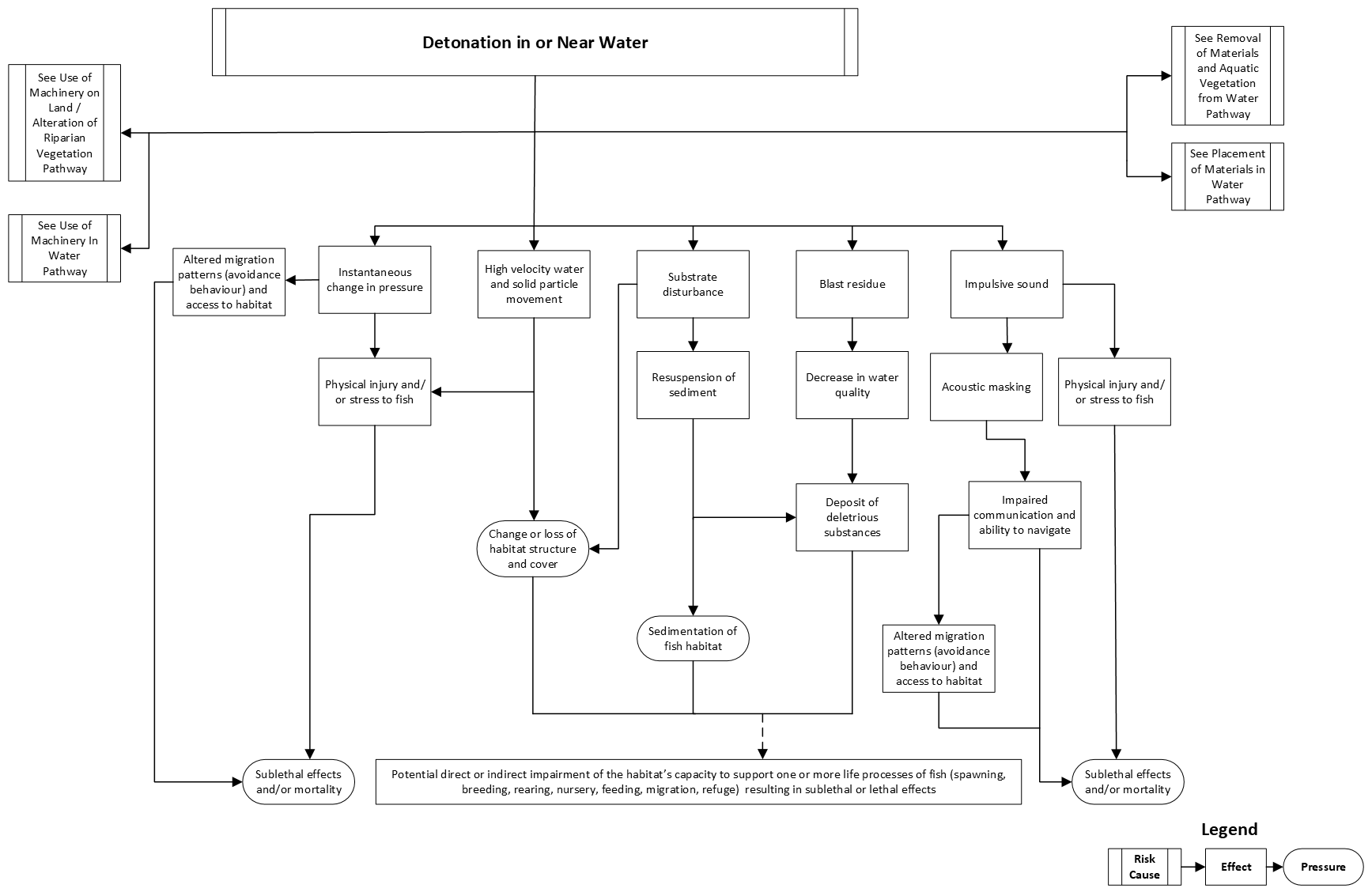
This pathway illustrates the chain of events that takes place in an aquatic ecosystem when explosives are detonated in or near water. Common works, undertakings and activities (WUAs) that involve detonating explosives include:
- geotechnical surveys
- construction
- repair and maintenance of infrastructure
- road construction
- pipeline installation
- mines and mining exploration
If not managed, detonation in or near water can result in:
- sedimentation of fish habitat
- changes to, or losses of:
- habitat structure and cover
These pressures have the potential to impair the habitat’s capacity to support the life processes of fish. Sublethal effects to fish (for example, injury, stress, impaired communication and navigation and migration) and fish mortality are also possible if protection measures are not put in place.
Introduction of underwater noise
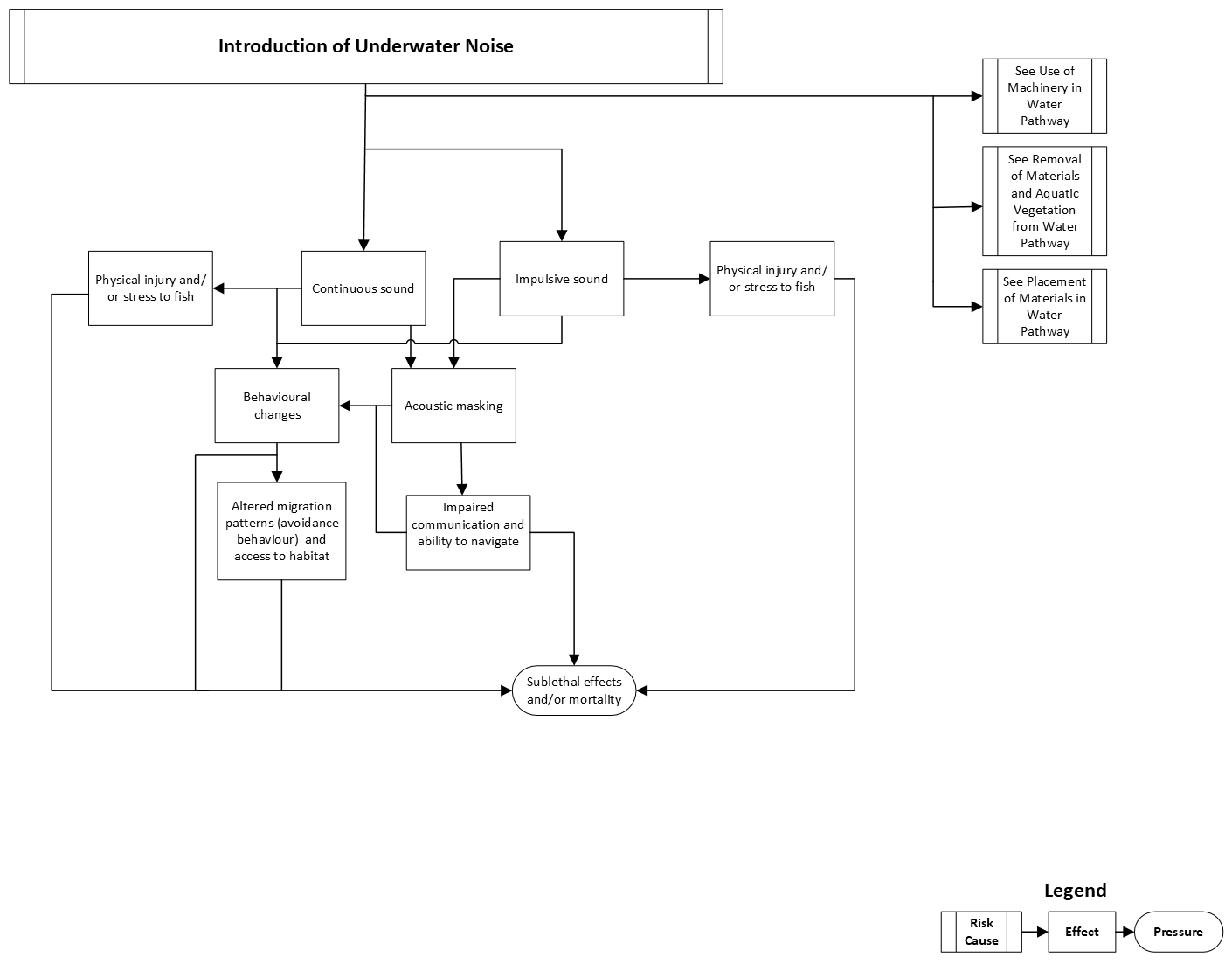
This pathway illustrates the chain of events that takes place in an aquatic ecosystem when noise is introduced. Common works, undertakings and activities (WUAs) that produce noise under water include:
- seismic and geotechnical surveys
- pile driving
- dredging
- drilling
- wind turbines
- tidal energy turbines
Sublethal effects to fish (for example, injury, stress, impaired communication and navigation and migration) and fish mortality are possible if protection measures are not put in place.
It is important to note that there are limitations to these PoE diagrams when applied to large scale, complex or unique projects that can cause additional risks and result in pressures not identified as endpoints in these diagrams. In these cases, other tools and resources may be needed for proponents to identify and describe risks, avoidance and mitigation measures and potential harmful impacts.
- Date modified: