Asian Shore Crab
Hemigrapsus sanguineus
Learn about Asian Shore Crab, including its identifying features, habitat, spread, impacts and our response.
Report it
If you think you have found an aquatic invasive species:
- do not return the species to the water
- take photos
- note:
- the exact location (GPS coordinates)
- the observation date
- identifying features
- contact us to report it
On this page
The Asian Shore Crab (Hemigrapsus sanguineus) is a small crab found in rocky areas where the ocean meets the land.
Origin and distribution
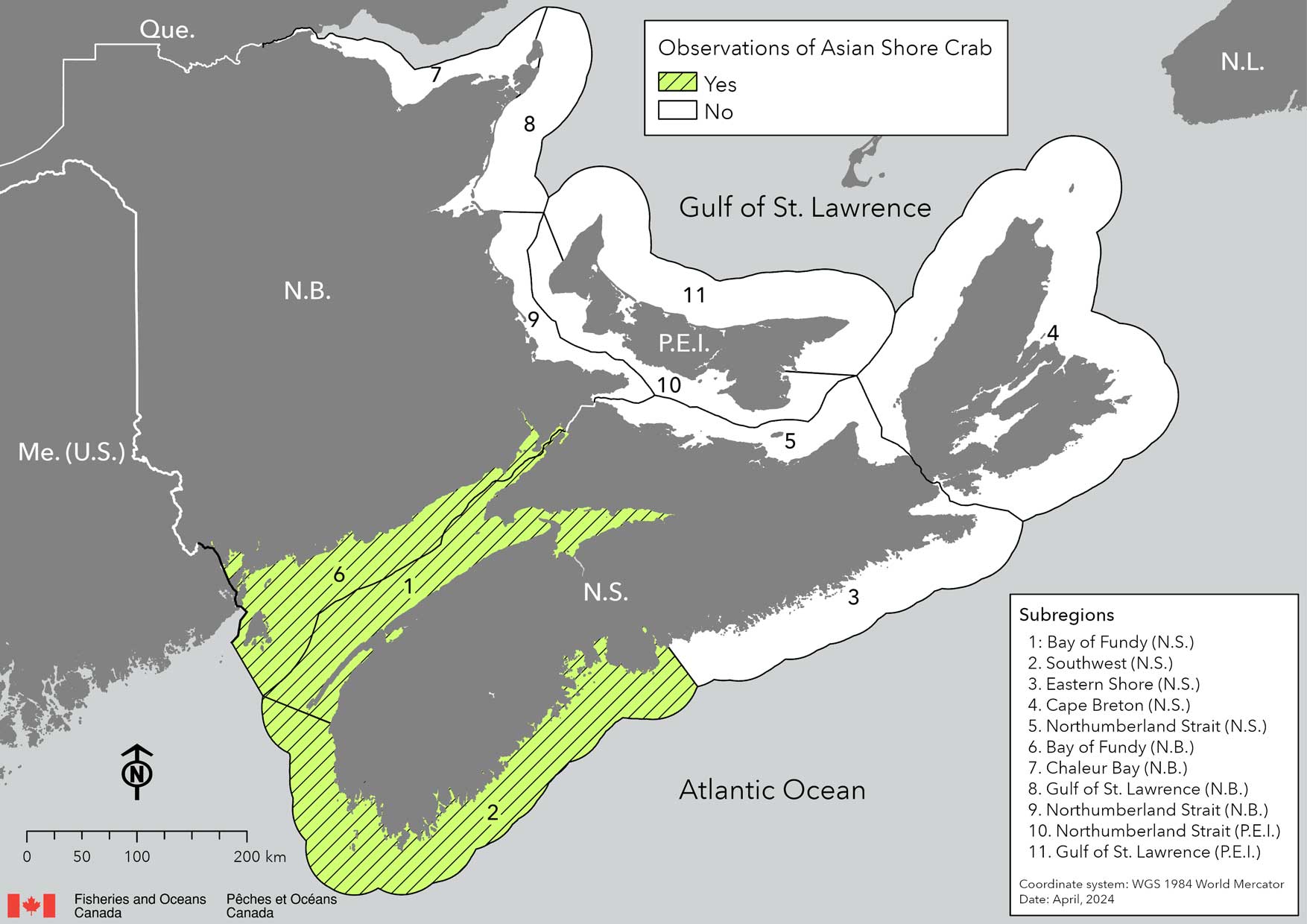
Observed distribution of Asian Shore Crab in subregions of Canada's Maritime provinces.
Note: Observation within a subregion does not mean the species is found throughout it. Lack of observation within a subregion does not mean the species is absent from that subregion. It means that it has not been observed there.
Asian Shore Crabs are native to northern Asia, with previously established populations in the United States and Europe, from the English Channel to Germany. The species has also been reported from the Black Sea and northern Adriatic Sea. In the United States, the Asian Shore Crab was first reported in New Jersey and has since established populations ranging from North Carolina to Maine.
The Asian Shore Crab was first detected in Canada in 2017 on the southern shores of Nova Scotia and New Brunswick. Its range now includes the Bay of Fundy coast of New Brunswick and multiple parts of Nova Scotia, spanning from St. Mary's Bay to Shelburne. The potential for spread is high since larvae are planktonic (free floating) for 16 to 54 days.
Natural dispersal of Asian Shore Crab occurs by means of the planktonic larvae carried on ocean currents, or as benthic adults living on the sea floor. Shipping vectors are typically implicated in dispersal outside the native range.
Identifying features
- a small hard bubble at the crux of its claws (males only)
- three spines along each side of its shell (carapace)
- the light-and-dark banding pattern on its legs
- its colour, which is mottled or dotted with reddish brown, greenish, or dark purple areas
- the small, dark purple-red dots on its dorsal (i.e. top) side
- its size: the maximum carapace width is around 4.4 centimetres
The Asian Shore Crab shares similar features with the European Green Crab, but is smaller, with 3 spines along each side of its carapace where a European Green Crab has 5.
If you think you have seen an Asian Shore Crab, report it.
Habitat
Asian Shore Crab native habitat consists of low-energy, intertidal, boulder/cobble beaches. The crabs also use:
- sand/pebble beaches
- mussel beds
- eelgrass beds and salt marshes
- rock jetties
- wooden bulkheads and pilings
- submerged and floating aquaculture gear (cages and spat collectors)
They move to subtidal depths during winter.
Impacts
Ecological impacts
Asian Shore Crabs are generalist omnivores known to consume:
- molluscs (like mussels, clams, and snails)
- small crustaceans
- polychaetes
- algae
In the USA, the Asian Shore Crab may reach population densities greater than 300 per square meter and have the potential to impact multiple species in the intertidal and subtidal zones by out-competing for food.
Socio-economic impacts
No significant impact to aquaculture has been identified, but Asian Shore Crab:
- have been found in fishing gear
- are known to consume mussels and oysters
- may compete with some aquaculture species for food and habitat
Government action
We are working to complete field work and a risk assessment to fully assess the distribution of the species and determine next steps.
Fisheries and Oceans Canada previously conducted a Biological Synopsis on this species in 2012.
Photo gallery
- Date modified:



